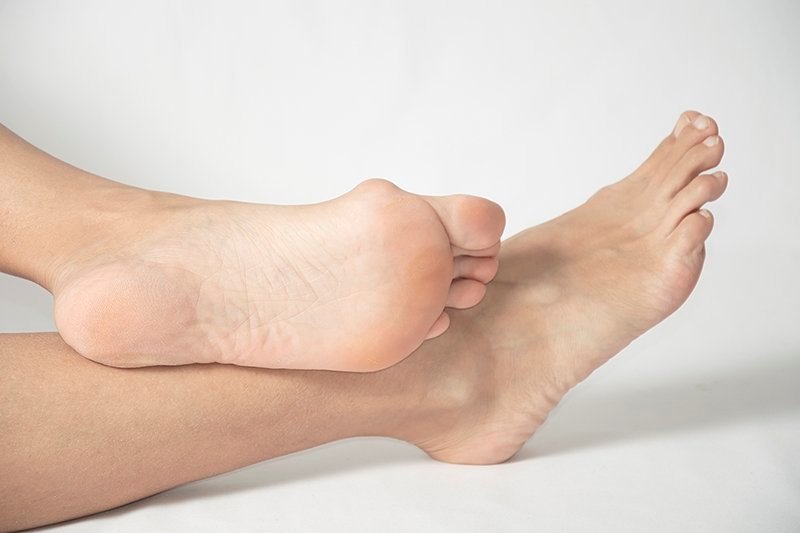
Bunion is a bone bump. It forms on the joint of the big toe. The medical name for this joint is the metatarsophalangeal joint (MTP).
Bunion occurs when the bones in the front of the foot move out of place. As a result, the tip of the big toe penetrates the small toes. This causes the joint at the base of the big toe to bulge. This happens slowly over time, and eventually it enlarges and bulges out. As a result, the big toe may turn inward, sometimes so much so that it overlaps the neighboring toe. The skin over the bunion may be red and painful.
Bunion occurs in about one in three Americans. It mostly affects the elderly. It is not uncommon for it to occur in adolescents as well. It occurs most often in girls between the ages of 10 and 15. Boys can also be susceptible to the disease. Unlike adults, young people with bunions can usually move their big toe, but it still hurts. Teenagers usually get bunions, not for health reasons, but because it runs in the family. Bursitis can form on one or both feet.

Symptoms
The most obvious signs and symptoms of bunions include:
- A bulging bump on the outside of the base of the big toe
- Swelling, redness and soreness around the joint of the big toe
- Calluses or corns – these often form where the first and second toes rub against each other
- Constant pain or pain that comes and goes
- Restricted mobility of the big toe
What are the types of bunions?
Bunions on the big toe are the most common. Other types include:
- Port bunionitis: Also called bunionitis, this type of bursitis forms on the outside of the base of the little (pinky) toe.
- Congenital: Some children are born with bunion.
- Juvenile or adolescent: Teenagers and young adults between the ages of 10 and 15 can get bunions.
What causes
There are many theories about how bunions develop, but the exact cause is unknown.
Probable factors include:
- Hereditary type of foot
- Stress or trauma to the foot
- Deformities present at birth
Experts disagree about footwear. Shoes have not been proven to affect bunions. But this factor is not excluded and is one of the main
Bursitis has been linked to arthritis. For example, inflammatory forms like rheumatoid arthritis.

Risk factors
These factors might increase your risk of bunions:
- High heels. High heels cause the toes to rest against the front of the shoe. This can lead to crowded toes. A consequence of this is bunions.
- Inappropriate shoes. It is not recommended to wear very tight, narrow, sharp-toed shoes. Any shoe in which the foot feels uncomfortable is dangerous.
- Rheumatoid arthritis. This disease increases the tendency for bunions to form.
- Heredity. Hereditary problems with the structure and anatomy of the foot are another threat.
What to do with bunions?
Proper-fitting footwear is key to preventing bunions or keeping an existing bunion from getting worse. Your healthcare provider can offer tips on how to select appropriate orthopedic sandals.
- The best choice in this case is Orthopedic Bunion Correction Sandals which are specially developed with a three arch support and a soft sole to keep your feet comfortable, healthy and safe.
- The protective pads soothe the pain under your toes. Walking with them is much easier. They are not hard to find. They are always available at the drugstore. Be sure to test them first. The wrong pad can make the pain worse.
- Put ice on it. It helps with the swelling. But do not put pure ice directly on the skin. Use a towel or a special pouch.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. The classic ibuprofen or naproxen. Or your other favorite active pain relievers. They will help you reduce pain and swelling.
- Providing rest. You will have to reduce the strain on the sore spot. Stressing the sore joint will make the problem worse.
- Fixing the joint. Use elastic bandages, plasters for fixation. It will become much easier.
- Folk methods of treatment of bursitis. Time-tested recipes effectively cope with different forms of this disease.
It is very important to look after the condition of our feet. It is necessary to prevent all diseases, not to treat them later. Preventing the health of our feet is much easier than it seems.
Conclusion
Bursitis is a relatively common musculoskeletal pathology that can be treated well with proper attention. In general, you should buy sandals with a wide toe box and soft soles. Avoid shoes that are narrow and pointed at the tip, and high heels that put pressure on the front of the foot. If you have flatfeet or another inherited structural foot problem, custom-fitted orthotics can help prevent, or slow the progression of, bunions. It can also be easily prevented by following the safety rules and using the proper equipment during sports activities.